
Infographic: The Armed Forces in the Constitution
Articles addressing the Armed Forces, constitute a major part of the Islamic Republic of Iran’s Constitution. These principles address the government’s responsibilities in military affairs, the Leader’s duties, powers, and authority over the armed forces, the Islamic Republic of Iran Army, the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, and the Law Enforcement Force. This infographic, prepared by the Research Institute of the Constitutional Council, provides a detailed overview of these constitutional provisions.
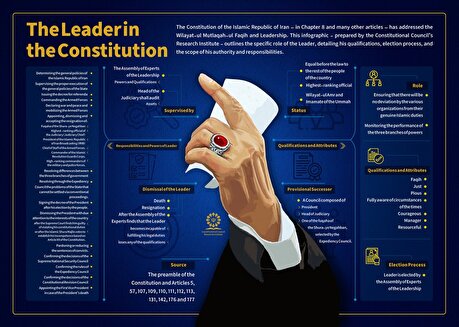
The Leader in the Constitution
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran – in Chapter 8 and many other articles – has addressed the Wilayat-ul Mutlaqah-ul Faqih and Leadership. This infographic - prepared by the Constitutional Council’s Research Institute - outlines the specific role of the Leader, detailing his qualifications, election process, and the scope of his authority and responsibilities.
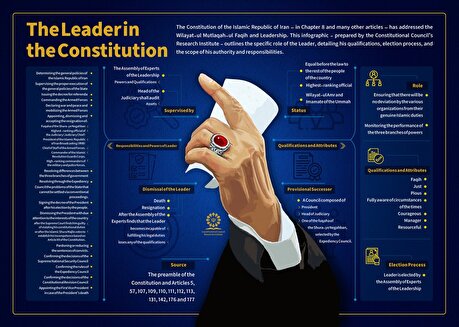
The Leader in the Constitution
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran – in Chapter 8 and many other articles – has addressed the Wilayat-ul Mutlaqah-ul Faqih and Leadership. This infographic - prepared by the Constitutional Council’s Research Institute - outlines the specific role of the Leader, detailing his qualifications, election process, and the scope of his authority and responsibilities.
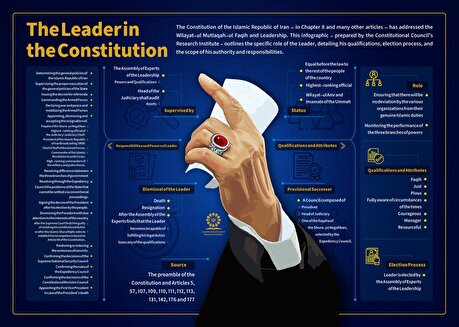
The Leader in the Constitution
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran – in Chapter 8 and many other articles – has addressed the Wilayat-ul Mutlaqah-ul Faqih and Leadership. This infographic - prepared by the Constitutional Council’s Research Institute - outlines the specific role of the Leader, detailing his qualifications, election process, and the scope of his authority and responsibilities.
Infographic: The Leader in the Constitution
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran – in Chapter 8 and many other articles – has addressed the Wilayat-ul Mutlaqah-ul Faqih and Leadership. This infographic - prepared by the Constitutional Council’s Research Institute - outlines the specific role of the Leader, detailing his qualifications, election process, and the scope of his authority and responsibilities.
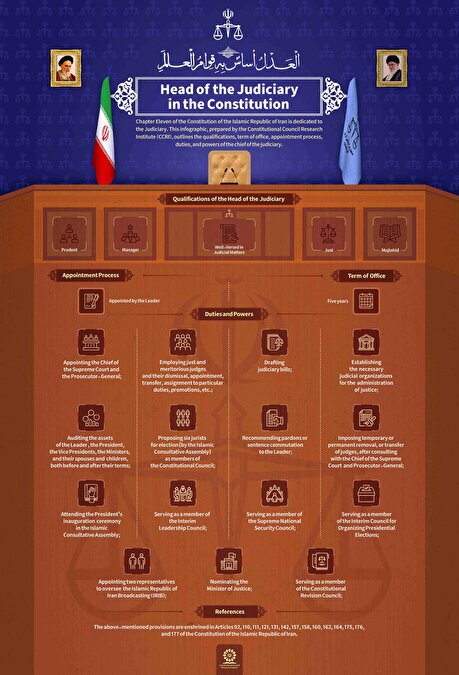
Infographic: Head of the Judiciary in the Constitution
Chapter 11 of the Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran is dedicated to the Judiciary. This infographic, prepared by the Constitutional Council Research Institute (CCRI), outlines the qualifications, term of office, appointment process, duties, and powers of the chief of the judiciary.

Infographic: Leader's expectations from presidential candidates
Leader of the Islamic Revolution Ayatollah Seyed Ali Khamenei expressed some expectations and requirements for the presidential candidates in referring to the issue of the 2021 presidential election in a televised speech on the occasion of the 32nd anniversary of Imam Khomeini’s demise. These expectations and requirements have been reviewed in this infographic.

Eight criteria for making the right choice
In addressing the Iranian nation in his annual speech on the first day of the Persian New Year this year, 1400 AH (March 2021), the Leader of the Islamic Revolution of Iran enumerated eight characteristics necessary in the country’s new president who is to be chosen in the upcoming elections. Emphasizing the importance of the enthusiastic participation of the people in the elections on June 18, 2021, Imam Khamenei stated that the solution to the serious problems of the country lies in making a good choice.

Infographic: Powers of Constitutional Council
The Iranian Constitution has granted the Constitutional Council the authority to interpret the Constitution, supervise elections (approval or disapproval of candidates seeking to run in local, parliamentary, presidential, and Assembly of Experts elections) and vet legislation passed by the country's Parliament.

Infographic: Members of the Constitutional Council
The Constitutional Council is comprised of twelve members: Six Faqihs and six jurists. The Faqihs (Islamic jurists) are appointed by the Leader of the Islamic Revolution, and the jurists are nominated by the head of the Judiciary and elected by Parliament.